With advances in the manufacturing of smaller and smaller components, there is a need for measurements at that scale to ensure that best accuracy is maintained. If you require measurement at the nano scale, or one billionth of a meter, then choosing the right technology will be high on your priority list. You want to make the most informed decision when choosing the equipment for measurements that are this important.
In general, there are two different types of nano-measurement technology, contact-based and optical-based. Here is a bit about each type of nano-measurement technology to help you determine which measurement option is the best fit for your application:
How do contact-based nano-measurements work?
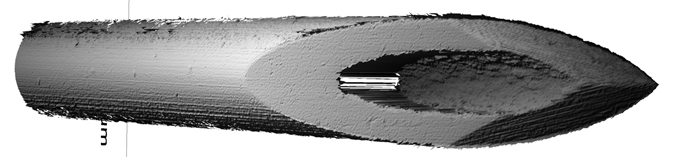
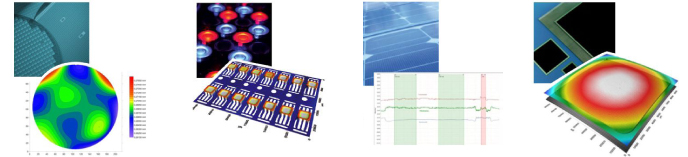
 As the name suggests, this type of nano measurement solution will come in contact with the piece to be measured in order to determine its dimensions. The two main types of equipment capable of these measurements are stylus profilometers and the atomic force microscope. Both have been in use for some time and use extremely sensitive styluses to collect the measurement data required.
As the name suggests, this type of nano measurement solution will come in contact with the piece to be measured in order to determine its dimensions. The two main types of equipment capable of these measurements are stylus profilometers and the atomic force microscope. Both have been in use for some time and use extremely sensitive styluses to collect the measurement data required.
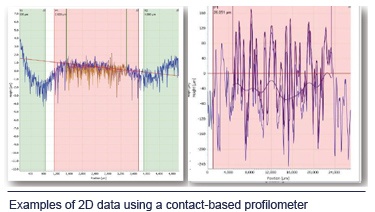
This type of nano-measurement is ideal if you need to measure a surface with a high aspect ratio since this can be a difficult to accomplish with optical-based solutions. These solutions have been around for a while so they are a tried and true way of measuring, and these methods are practically good at delivering 2-D data.
How do optical-based nano-measurements work?
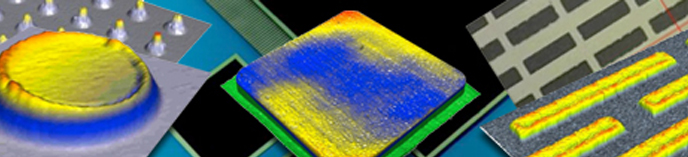
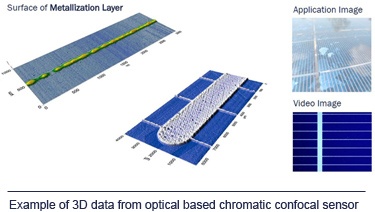 Optical-based nano-measurement technologies are quickly becoming the go-to devices for measurements at the nano level. Since these techniques do not touch the surface of the piece to be measured, there is no risk that small or delicate parts will be damaged or moved during measurement. As an added feature, optical measurements are also done more quickly than traditional contact-based measurements, and typically have an innate ability to obtain 3D measurements in addition to 2D data.
Optical-based nano-measurement technologies are quickly becoming the go-to devices for measurements at the nano level. Since these techniques do not touch the surface of the piece to be measured, there is no risk that small or delicate parts will be damaged or moved during measurement. As an added feature, optical measurements are also done more quickly than traditional contact-based measurements, and typically have an innate ability to obtain 3D measurements in addition to 2D data.
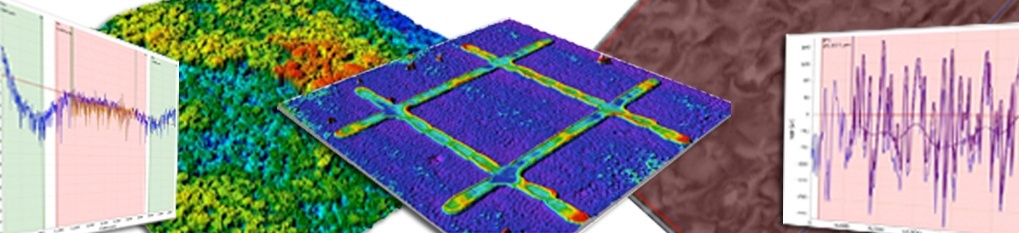
There are several methods used in optical-based nano-measurement; among them are triangulation, white light interferometry, confocal microscopes and chromatic confocal sensors. The commonality of these methods is the use of light that is emitted and then re-captured in a manner that will allow the equipment to make the extremely accurate measurements necessary to measure at the nano level.
Which type of nano-measurement is right for you?
Each of the methods listed above has benefits and drawbacks that you will need to weigh in your decision; and the decision greatly depends on what you will be measuring. As stated, contact-based measurements can make very high resolution measurements because they come in contact with the surface, but this also risks damage for delicate parts and can be much more expensive to operate.
By contrast, optical-based measurements do not risk damage to parts as only light comes in contact with the pieces, and are capable of measuring much more quickly that the contact-based methods. The drawback can be some difficulty with surfaces with high aspect ratios; such as surfaces with many features such as grooves, sharp edges, holes, steps, steep slopes or channels. So it is important to know what you will be measuring when you are choosing between the nano-measurement equipment available.
This is where the dedicated team at Q-PLUS Labs can help. Our experts have taken the time to know all the aspects of each piece of equipment best suited for each customer's application in order to recommend the best fit measurement equipment. Whether you need measurement services or help finding the right equipment for in-house measurements, our team can help. Contact us today to schedule a consultation.